US Energy Storage Market: Ready for 50 GW Solar Capacity by 2027?

The US energy storage market faces a significant challenge in supporting the planned 50 GW of new solar capacity by 2027, requiring substantial growth and overcoming hurdles in technology, policy, and grid infrastructure.
Is the current US energy storage market robust enough to handle the surge of renewable energy coming with the planned 50 GW of new solar capacity by 2027? The answer is complex, involving technology, policy, and infrastructure.
Understanding the US Energy Storage Landscape
The US energy storage market is undergoing rapid transformation. Driven by increasing renewable energy adoption, supportive policies, and technological advancements, it’s becoming a crucial component of the nation’s energy infrastructure. However, significant challenges remain in scaling up to meet future demand.
Current Energy Storage Capacity
As of late 2024, the US has deployed a considerable amount of energy storage, but is it enough? Understanding the current baseline is critical for projecting future needs.
- California leads the nation in installed energy storage capacity, primarily lithium-ion batteries.
- Texas is rapidly expanding its storage capacity, driven by the increasing penetration of wind and solar energy.
- Other states, such as Arizona, Florida and New york , are also investing heavily in energy storage projects.
Types of Energy Storage Technologies
Different energy storage technologies offer various benefits and drawbacks. Examining the mix of technologies in use is essential.
- Lithium-ion batteries dominate the market due to their high energy density and declining costs.
- Pumped hydro storage remains a significant contributor, although new projects are limited by geographic constraints.
- Emerging technologies like flow batteries, compressed air energy storage (CAES), and thermal storage are gaining traction, but still constitute a small portion of the overall market.
In conclusion, while the US energy storage market is growing, it still needs significant expansion and diversification to adequately support the planned solar capacity additions. Overcoming technological limitations and policy hurdles will be crucial.
The 50 GW Solar Capacity Target: A Realistic Goal?
The ambitious goal of adding 50 GW of new solar capacity by 2027 represents a significant step toward decarbonizing the US energy sector. However, achieving this target requires careful planning and execution, considering various factors that could influence its feasibility.
Factors Driving Solar Capacity Growth
Several factors are contributing to the rapid expansion of solar energy in the US. Understanding these drivers is vital for assessing the target’s attainability.
- The declining cost of solar photovoltaic (PV) technology makes it increasingly competitive with traditional energy sources.
- Federal and state policies, such as the Investment Tax Credit (ITC) and Renewable Portfolio Standards (RPS), incentivize solar development.
- Growing demand for clean energy from corporations and consumers is fueling investment in solar projects.
Potential Challenges to Meeting the Target
Despite the positive trends, several challenges could hinder the achievement of the 50 GW solar capacity target.
- Supply chain constraints, including shortages of critical materials like silicon and semiconductors, could delay project timelines.
- Interconnection bottlenecks, resulting from grid congestion and long queues for grid access, could slow down the deployment of new solar capacity.
- Land use conflicts and community opposition to large-scale solar projects could create permitting delays and project cancellations.
Overall, while the 50 GW solar capacity target is ambitious but potentially achievable, addressing the identified challenges proactively is essential to ensure successful implementation. A coordinated approach involving government, industry, and communities is crucial.
The Role of Energy Storage in Integrating Solar Power
Energy storage plays a critical role in integrating solar power into the grid. As solar energy generation fluctuates with weather conditions and time of day, energy storage provides a means to smooth out these fluctuations and ensure a reliable supply of electricity.
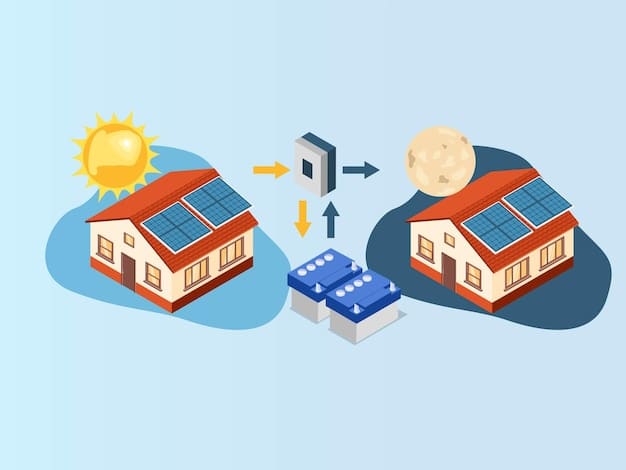

Balancing Supply and Demand
Energy storage helps balance supply and demand by storing excess solar energy during periods of high production and releasing it during periods of low production or high demand.
Enhancing Grid Stability
Energy storage provides essential grid services, such as frequency regulation and voltage support, which enhance the stability and reliability of the electricity grid.
Reducing Curtailment
Energy storage can reduce the amount of solar energy that is curtailed, or wasted, due to grid constraints or oversupply. By storing excess solar energy, it can be used later when demand is higher.
In summary, energy storage is essential for integrating large amounts of solar power into the grid. Its ability to balance supply and demand, enhance grid stability, and reduce curtailment makes it a critical component of a clean energy future.
Analyzing the Current Energy Storage Market Capacity
The current energy storage market capacity needs careful examination to determine its readiness to support the planned 50 GW of new solar capacity. Assessing the existing infrastructure, ongoing projects, and planned investments is crucial.
Existing Energy Storage Infrastructure
The existing energy storage infrastructure in the US is composed of various technologies, with lithium-ion batteries dominating new deployments.
Ongoing Energy Storage Projects
Numerous energy storage projects are currently under development across the US, driven by state mandates, federal incentives, and utility investments.
Planned Investments in Energy Storage
Significant investments are planned for energy storage deployment in the coming years, reflecting the growing recognition of its importance in the energy transition.
In conclusion, while the energy storage market is expanding rapidly, it is essential to monitor its growth trajectory closely to ensure it can keep pace with the deployment of new solar capacity. Strategic investments and policy support will be needed to accelerate the development of energy storage infrastructure.
Policy and Regulatory Support for Energy Storage
Policy and regulatory support plays a crucial role in fostering the growth of the energy storage market. Supportive policies can provide incentives, reduce barriers to entry, and create a level playing field for energy storage technologies.
Federal Policies and Incentives
Federal policies, such as the Investment Tax Credit (ITC) and the Energy Storage Grand Challenge, provide significant incentives for energy storage deployment.
State Policies and Mandates
State policies, such as energy storage mandates and Renewable Portfolio Standards (RPS) with storage carve-outs, drive the deployment of energy storage at the state level.
Regulatory Framework for Energy Storage
The regulatory framework for energy storage, including rules governing interconnection, market participation, and grid services, can significantly impact its economic viability.
In summary, supportive policies and a well-designed regulatory framework are essential for accelerating the deployment of energy storage. Governments at all levels must work together to create a conducive environment for energy storage investment and innovation.
Challenges and Opportunities in the Energy Storage Market
The energy storage market faces several challenges and opportunities that will shape its future development. Addressing these challenges and capitalizing on the opportunities is crucial for realizing the full potential of energy storage.
Technological Challenges
Technological challenges include improving the performance, reducing the cost, and enhancing the safety of energy storage technologies. Research and development efforts are needed to overcome these hurdles.
Economic Challenges
Economic challenges include reducing the upfront costs of energy storage, developing viable business models, and ensuring cost-effective grid integration.
Market Design Challenges
Market design challenges include creating fair and transparent market rules that properly value the services provided by energy storage, such as frequency regulation and capacity.
In conclusion, while the energy storage market faces significant challenges, the opportunities are even greater. By addressing the technological, economic, and market design hurdles, energy storage can play a transformative role in the energy transition, enabling a cleaner, more reliable, and more resilient energy system.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| ☀️ Solar Target | 50 GW new solar capacity by 2027 requires substantial support. |
| 🔋 Storage Need | Energy storage is critical for solar integration and grid stability. |
| 🏛️ Policy Impact | Policies and regulations significantly drive storage deployment. |
| ⚡️ Challenges | Tech, economic, and market hurdles need to be addressed. |
FAQ
▼
The primary goal is to significantly decarbonize the US energy sector, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating climate change impacts by increasing renewable energy generation.
▼
Energy storage is crucial because it addresses the intermittency of solar energy, ensuring a stable and reliable power supply by storing excess energy for later use during periods of low sunlight.
▼
Key policy drivers include the Investment Tax Credit (ITC), state-level energy storage mandates, and Renewable Portfolio Standards (RPS) with storage carve-outs, incentivizing investment and deployment.
▼
Technological challenges include improving energy density, reducing costs, enhancing safety, and extending the lifespan of storage technologies like lithium-ion batteries and flow batteries.
▼
Energy storage enhances grid stability by providing essential services like frequency regulation, voltage support, and black start capabilities, ensuring the grid can handle fluctuations and recover from outages.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while the US energy storage market is growing, significant challenges remain in ensuring it’s ready to support the planned 50 GW of new solar capacity by 2027. Overcoming these challenges requires continued innovation, supportive policies, and strategic investments in energy storage infrastructure.