Energy Storage Maintenance 2026: Extend Lifespan by 5 Years

Proactive maintenance of energy storage systems in 2026 is vital for extending their operational lifespan by up to five years, safeguarding investment, and ensuring consistent, reliable energy delivery through strategic interventions.
As the energy landscape rapidly evolves, the longevity and efficiency of energy storage systems have become paramount. In 2026, energy storage maintenance 2026 is not merely a reactive measure but a strategic imperative designed to extend operational lifespans by up to five years, ensuring robust performance and maximizing return on investment.
Understanding the Evolving Landscape of Energy Storage in 2026
The year 2026 marks a significant juncture in energy storage technology. Advancements in battery chemistry, particularly solid-state and flow batteries, alongside sophisticated grid integration software, have fundamentally altered how these systems operate and, consequently, how they need to be maintained. The sheer scale and complexity of these deployments demand a more nuanced approach than ever before.
The imperative to extend the lifespan of these critical assets stems from both economic and environmental considerations. Financially, a longer lifespan translates to a lower levelized cost of storage (LCOS), making renewable energy more competitive. Environmentally, maximizing the operational years of an energy storage system reduces the need for premature replacement and the associated resource consumption and waste generation.
The Role of Predictive Analytics and AI
In 2026, predictive analytics and artificial intelligence are no longer nascent technologies but integral components of effective energy storage maintenance. These tools analyze vast datasets from system sensors, identifying subtle anomalies that could indicate impending failure long before they manifest as critical issues. This proactive stance is a cornerstone of current maintenance best practices.
- Early fault detection: AI algorithms can pinpoint deviations from normal operating parameters.
- Optimized maintenance scheduling: Predictive models forecast component wear and recommend service intervals.
- Performance degradation forecasting: Anticipate capacity fade and efficiency losses to plan upgrades.
By leveraging these sophisticated tools, operators can move beyond scheduled preventative maintenance to a more dynamic, condition-based approach, significantly reducing downtime and extending the useful life of their assets. This shift is crucial for meeting the ambitious energy transition goals set for the coming decade.
Critical Consideration 1: Advanced Battery Management System (BMS) Monitoring
In 2026, the Battery Management System (BMS) is the brain of any energy storage installation, constantly overseeing battery health and performance. Advanced BMS solutions now incorporate machine learning to predict degradation patterns and optimize charging/discharging cycles, making their monitoring more critical than ever. Ignoring the detailed insights provided by these systems is a common pitfall that can severely impact lifespan.
Regular, in-depth analysis of BMS data is essential. This isn’t just about checking for alarms; it involves scrutinizing trends in cell voltage, temperature, current, and state of charge (SoC) and state of health (SoH) across the entire battery pack. Discrepancies, however minor, can signal underlying issues that, if unaddressed, lead to accelerated degradation of individual cells and, subsequently, the entire system.
Leveraging Real-time Data for Proactive Intervention
Modern BMS platforms offer real-time data streaming and sophisticated visualization tools. Operators in 2026 must utilize these capabilities to their fullest potential. Instead of merely logging data, the focus should be on interpreting it to make informed, proactive maintenance decisions. This includes identifying cell imbalances, thermal runaway risks, and potential communication errors within the system.
- Continuous cell voltage monitoring to detect imbalances.
- Temperature gradient analysis across battery modules.
- Anomaly detection in charging and discharging current profiles.
A robust monitoring strategy, underpinned by a highly functional BMS, acts as the first line of defense against premature system failure. It enables timely interventions that can correct minor issues before they escalate into costly and time-consuming problems, directly contributing to extending the system’s operational life.
Critical Consideration 2: Optimized Thermal Management Strategies
Temperature is a primary determinant of battery lifespan, and in 2026, optimized thermal management is paramount for energy storage systems. Operating batteries outside their ideal temperature range significantly accelerates degradation, reducing capacity and cycle life. This applies to both excessively high and low temperatures, though overheating is often the more prevalent concern in many operational environments.
Modern energy storage installations integrate advanced cooling and heating systems, from liquid cooling loops to sophisticated HVAC units. The maintenance of these thermal management systems is as crucial as the batteries themselves. Regular checks of coolant levels, pump functionality, fan operation, and heat exchanger efficiency are non-negotiable to ensure optimal battery operating conditions.
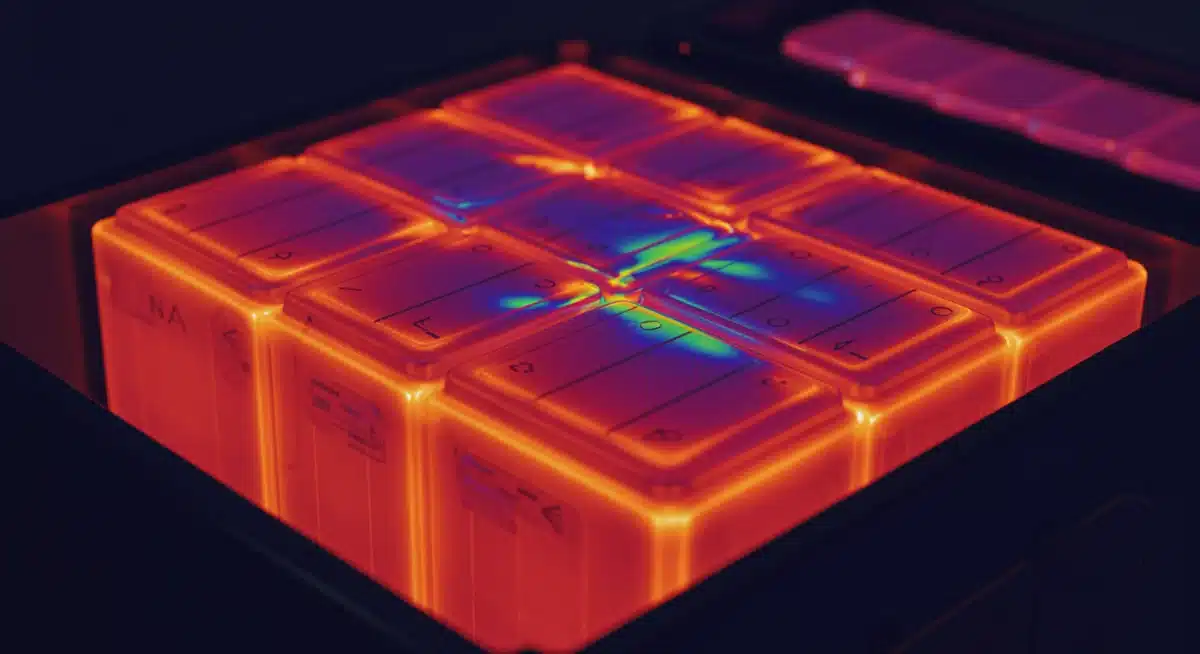
Implementing Advanced Cooling Technologies
The latest generation of energy storage systems benefits from innovative cooling solutions that offer greater precision and efficiency. These include phase-change materials, immersion cooling, and predictive thermal control algorithms that anticipate temperature fluctuations based on operational forecasts and environmental conditions. Proper calibration and maintenance of these systems are essential.
- Regular inspection of coolant lines for leaks and blockages.
- Verification of sensor accuracy for temperature readings.
- Software updates for thermal control algorithms to adapt to changing conditions.
By meticulously maintaining thermal management systems, operators can ensure that batteries consistently operate within their optimal temperature window, thereby mitigating one of the most significant factors contributing to accelerated degradation. This directly translates into a longer, more reliable service life for the entire energy storage asset.
Critical Consideration 3: Proactive Power Conversion System (PCS) Maintenance
The Power Conversion System (PCS) is the interface between the battery and the grid, responsible for efficient energy flow. In 2026, PCS units are highly sophisticated, often incorporating advanced inverters, transformers, and control electronics. Neglecting PCS maintenance can lead to inefficiencies, increased stress on battery components, and ultimately, system failure.
Regular inspections of PCS components should include checking for loose connections, signs of overheating, dust accumulation, and the integrity of cooling fans. Firmware updates are also crucial, as manufacturers frequently release enhancements that improve efficiency, reliability, and grid compliance. A well-maintained PCS ensures stable power delivery and protects the battery from electrical anomalies.
Ensuring Grid Code Compliance and Optimization
As grid regulations continue to evolve, particularly regarding ancillary services and grid stability, PCS units must be kept up-to-date. This involves not only hardware maintenance but also software configuration and calibration to ensure compliance with the latest grid codes. Failure to do so can result in penalties or even disconnection from the grid, severely impacting revenue streams.
- Calibration of voltage and frequency control parameters.
- Regular testing of protective relays and circuit breakers.
- Verification of communication protocols with grid operators.
A proactive approach to PCS maintenance ensures not only its own longevity but also supports the overall health and performance of the entire energy storage system. By keeping the PCS in peak condition, operators safeguard the battery’s operational integrity and optimize its interaction with the electrical grid.
Critical Consideration 4: Cybersecurity for Connected Energy Assets
With energy storage systems increasingly connected to the internet for remote monitoring and control, cybersecurity has become a critical maintenance consideration in 2026. A compromised system can lead to operational disruptions, data breaches, and even physical damage. Protecting these assets from cyber threats is as vital as physical maintenance.
Implementing robust cybersecurity protocols involves more than just strong passwords. It requires regular security audits, penetration testing, and continuous monitoring for suspicious activity. All network-connected components, from the BMS to the PCS and site controllers, must be secured against unauthorized access and malicious attacks.
Developing a Comprehensive Cybersecurity Strategy
An effective cybersecurity strategy for energy storage includes multiple layers of defense. This encompasses network segmentation, intrusion detection systems, and regular employee training on security best practices. Given the dynamic nature of cyber threats, this is an ongoing process, not a one-time setup.
- Regular software and firmware updates to patch vulnerabilities.
- Implementation of multi-factor authentication for all remote access.
- Incident response planning for rapid containment and recovery from attacks.
By prioritizing cybersecurity as a core maintenance function, operators can protect their energy storage investments from increasingly sophisticated digital threats. This ensures the continuous, secure operation of these vital assets, maintaining energy reliability and preventing costly disruptions.
Critical Consideration 5: Regular Structural and Environmental Inspections
Beyond the internal workings of batteries and electronics, the physical infrastructure and environmental conditions surrounding energy storage systems are equally important for longevity. In 2026, systems are often housed in dedicated containers or buildings, and their structural integrity and environmental controls directly impact performance and safety.
Routine inspections should cover the physical enclosure, fire suppression systems, ventilation, and any associated civil engineering. Corrosion, pest infestation, and extreme weather exposure can all compromise system integrity. Ensuring a stable and protected environment prevents external factors from accelerating internal component degradation.
Maintaining a Controlled Operating Environment
The operational environment plays a significant role in battery health. This includes not just temperature, but also humidity, dust, and vibration. Regular cleaning, calibration of environmental sensors, and proactive repairs to structural elements or climate control systems are essential. This comprehensive approach safeguards the entire installation.
- Inspection of fire suppression systems and emergency exits.
- Checks for water ingress, mold, or structural damage.
- Verification of ventilation system functionality and air quality.
By conducting thorough structural and environmental inspections, operators can address potential hazards before they impact the energy storage system. This holistic maintenance approach ensures a safe, stable, and optimal operating environment, contributing significantly to extending the overall lifespan of the assets.
Critical Consideration 6: Data-Driven Performance Analysis and Reporting
In 2026, simply monitoring system health is not enough; comprehensive data-driven performance analysis and reporting are vital for optimizing energy storage systems. This involves not only collecting vast amounts of operational data but also interpreting it to identify areas for improvement, validate maintenance strategies, and project future performance.
Regular performance reviews should involve comparing actual system output against expected benchmarks, analyzing round-trip efficiency, and tracking capacity degradation over time. These reports provide invaluable insights into the effectiveness of current maintenance protocols and highlight where adjustments are needed to meet the goal of extending lifespan by five years.
Implementing Advanced Analytics Platforms
The advent of advanced analytics platforms specifically designed for energy storage enables deeper insights than ever before. These platforms can correlate operational data with external factors like weather patterns, grid demand, and market prices to provide a holistic view of system performance and profitability. Utilizing such tools is now a standard practice for leading operators.
- Tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) like availability and reliability.
- Benchmarking against industry standards and similar installations.
- Forecasting future capacity and degradation curves based on historical data.
Through rigorous data-driven performance analysis, operators can gain a clear understanding of their energy storage assets’ health and efficiency. This enables them to make informed decisions, refine maintenance schedules, and implement strategic upgrades that directly contribute to maximizing both the lifespan and economic value of their systems.
| Key Consideration | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| Advanced BMS Monitoring | Crucial for real-time battery health insights and proactive issue detection to prevent degradation. |
| Optimized Thermal Management | Ensures batteries operate within ideal temperature ranges to significantly extend their lifespan. |
| Proactive PCS Maintenance | Maintains efficient energy conversion, protecting batteries and ensuring grid compliance. |
| Cybersecurity for Assets | Protects connected systems from digital threats, preventing disruptions and data breaches. |
Frequently Asked Questions About Energy Storage Maintenance
In 2026, energy storage systems are larger, more complex, and integral to grid stability. Advanced battery chemistries and sophisticated software demand precise, proactive maintenance to maximize their significant investment and ensure reliability in a rapidly evolving energy landscape.
Predictive analytics uses AI to analyze operational data, identifying subtle anomalies that indicate potential issues before they become critical. This enables operators to schedule maintenance precisely when needed, preventing premature wear and extending the system’s useful life.
Key practices include regular checks of advanced cooling systems like liquid loops, verifying sensor accuracy, and implementing software updates for thermal control algorithms. Maintaining optimal operating temperatures is crucial for preventing accelerated battery degradation and ensuring longevity.
Modern ESS are connected assets, making them vulnerable to cyber threats. Cybersecurity maintenance, including software updates, security audits, and network segmentation, protects against operational disruptions, data breaches, and potential physical damage, ensuring system integrity and reliability.
Data-driven analysis provides deep insights into system efficiency, degradation rates, and operational effectiveness. By tracking KPIs and benchmarking, operators can validate maintenance strategies, identify areas for improvement, and make informed decisions to optimize performance and extend lifespan.
Conclusion
Effectively managing energy storage systems in 2026 requires a sophisticated, multi-faceted approach that goes far beyond traditional maintenance routines. By diligently addressing the critical considerations outlined – from advanced BMS monitoring and optimized thermal management to robust cybersecurity and data-driven performance analysis – operators can significantly extend the operational lifespan of their assets by five years or more. This proactive and strategic investment in maintenance not only safeguards valuable infrastructure but also ensures the continued reliability, efficiency, and economic viability of energy storage as a cornerstone of the global energy transition.





