Grid Resilience 2026: Preventing Outages, Saving 15% Annually

By 2026, advanced energy storage systems are poised to significantly enhance grid resilience, preventing costly power outages and delivering an estimated 15% annual financial savings for businesses.
In the rapidly evolving landscape of 2026, the concept of grid resilience 2026 has become paramount, particularly for businesses grappling with the unpredictable nature of power supply. The promise of advanced energy storage isn’t just about environmental stewardship; it’s a critical financial imperative, offering a tangible shield against operational disruptions and a pathway to substantial annual savings.
The Imperative of Grid Resilience in 2026
The year 2026 marks a pivotal moment for energy infrastructure, with increasing demands and the growing threat of climate-related disruptions challenging traditional grid stability. Businesses, more than ever, recognize that power reliability is not merely a convenience but a cornerstone of their operational continuity and financial health.
The economic impact of power outages has escalated dramatically. From data centers to manufacturing plants, an unexpected blackout can translate into millions of dollars in lost revenue, damaged equipment, and compromised data. This reality underscores the urgent need for robust solutions that go beyond conventional backup systems.
Understanding the Evolving Threat Landscape
The threats to grid stability are multifaceted, ranging from severe weather events to cyberattacks and aging infrastructure. Each presents a unique challenge that traditional centralized grids struggle to address effectively.
- Extreme Weather Events: Hurricanes, wildfires, and ice storms are becoming more frequent and intense, causing widespread and prolonged power disruptions.
- Aging Infrastructure: Much of the existing grid infrastructure in the United States is decades old, making it vulnerable to failures and less efficient in handling modern energy demands.
- Cybersecurity Risks: The increasing digitalization of the grid introduces new vectors for cyberattacks that could cripple energy delivery systems.
Addressing these threats requires a proactive and adaptive approach, moving away from reactive responses to preventative measures. Grid resilience in 2026 is about building an energy ecosystem that can withstand and rapidly recover from disturbances, ensuring minimal impact on critical operations.
The imperative for grid resilience in 2026 extends beyond mere reliability; it encompasses economic stability and competitive advantage. Companies that invest in resilient energy solutions are better positioned to navigate an uncertain future, protecting their assets and ensuring uninterrupted service to their customers.
Advanced Energy Storage: A Game Changer for Stability
Advanced energy storage technologies are at the forefront of the revolution in grid resilience. These systems, encompassing everything from sophisticated battery arrays to innovative thermal storage solutions, provide the flexibility and responsiveness necessary to buffer the grid against fluctuations and outages. Their ability to store surplus energy and release it precisely when needed transforms the energy landscape.
Unlike traditional generators, modern energy storage systems offer instantaneous power, critical for preventing costly interruptions. They integrate seamlessly with renewable energy sources, maximizing their potential and further decentralizing power generation, which inherently boosts resilience. This distributed approach means that even if one part of the grid fails, localized energy supplies can maintain operations.
Key Technologies Driving the Shift
Several advanced energy storage technologies are leading the charge in enhancing grid stability. Each offers unique advantages, contributing to a more robust and flexible energy infrastructure.
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: These remain the dominant technology, offering high energy density and increasingly competitive costs, suitable for both short-duration and longer-duration storage needs.
- Flow Batteries: Promising for large-scale, long-duration storage, flow batteries separate power and energy components, allowing for flexible scaling.
- Solid-State Batteries: Emerging as a safer and potentially more energy-dense alternative, solid-state technology is gaining traction for future grid applications.
- Thermal Energy Storage: Utilizing materials to store heat or cold, these systems are particularly effective for industrial processes and district heating/cooling, reducing peak electricity demand.
The integration of these diverse storage technologies creates a multi-layered defense against grid instability. This diversification ensures that different types of energy demands can be met efficiently, from mitigating momentary voltage sags to providing hours of backup power during extended outages. The inherent modularity of many of these systems also allows for scalable deployment, adapting to specific business needs and grid requirements.
Ultimately, advanced energy storage is not just about holding power; it’s about intelligent energy management. These systems are often paired with sophisticated energy management software that optimizes charging and discharging cycles, ensuring maximum efficiency and economic benefit. This intelligent control is what truly elevates advanced energy storage to a game-changer for grid stability in 2026.
Preventing Outages: How Storage Fortifies Business Operations
The primary benefit of advanced energy storage for businesses is its unparalleled ability to prevent and mitigate power outages. By deploying these systems, companies can create a localized, resilient energy ecosystem that acts as a buffer against grid disruptions. This fortification translates directly into uninterrupted operations, safeguarding critical processes and data.
When the main grid experiences a fault or an outage, advanced energy storage systems can instantaneously switch to supplying power, often without any noticeable interruption to business activities. This seamless transition is crucial for industries where even a momentary power loss can have significant consequences, such as manufacturing, healthcare, and information technology.
Real-Time Response and Microgrid Integration
One of the most powerful features of advanced energy storage is its capacity for real-time response. These systems can detect grid anomalies and deploy power within milliseconds, effectively acting as a shock absorber for the electrical network. This rapid response prevents small disturbances from escalating into full-blown outages.
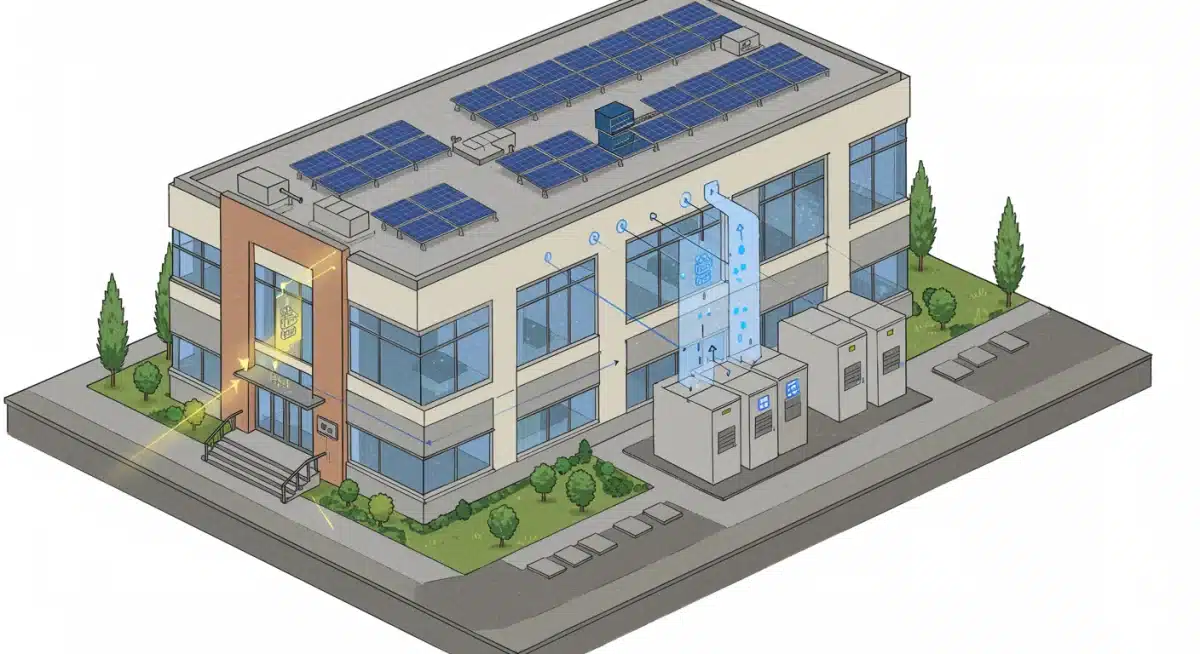

Furthermore, advanced energy storage is a foundational component of modern microgrids. Microgrids allow businesses to operate independently of the main grid during an outage, drawing power from their own generation sources (like solar panels) and stored energy. This creates an islanded mode of operation, providing complete energy independence when the grid falters.
- Seamless Transition: Automatic transfer switches ensure that power shifts from the grid to stored energy without disruption.
- Load Management: Systems can prioritize critical loads, ensuring essential operations remain powered even during prolonged events.
- Voltage and Frequency Support: Storage systems help stabilize voltage and frequency, protecting sensitive electronics from power quality issues.
The ability to maintain consistent power quality and supply not only prevents immediate losses but also protects valuable equipment from damage caused by power surges or brownouts. This preventative aspect significantly reduces maintenance costs and extends the lifespan of sensitive machinery.
In essence, advanced energy storage transforms a business’s vulnerability to grid instability into a position of strength. By preventing outages and enabling continuous operation, these systems ensure that businesses can maintain productivity, customer trust, and ultimately, their competitive edge, even in the face of widespread grid challenges.
Financial Impact: Estimated 15% Annual Savings for Businesses
Beyond outage prevention, advanced energy storage systems offer a compelling financial proposition for businesses, projecting an estimated 15% annual savings by 2026. This significant economic benefit stems from various mechanisms, primarily peak shaving, demand charge reduction, and optimized energy procurement.
Businesses often face high demand charges from utilities, which are based on their highest electricity consumption during a billing cycle, regardless of the average usage. Energy storage allows companies to draw power from their batteries during these peak periods, thereby reducing their demand from the grid and significantly lowering these charges.
Strategies for Cost Reduction
Implementing advanced energy storage allows businesses to employ several strategic approaches to minimize their energy expenditures. These strategies leverage the flexibility of stored energy to capitalize on market conditions and utility rate structures.
- Peak Shaving: Discharging stored energy during hours of highest electricity demand and prices, effectively ‘shaving’ off the most expensive consumption peaks.
- Time-of-Use Optimization: Charging batteries during off-peak hours when electricity is cheaper and discharging during on-peak hours, maximizing savings on variable rates.
- Ancillary Services: In some markets, businesses can participate in grid ancillary services, offering their stored energy capacity to help stabilize the grid and earning revenue in return.
The integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar, further amplifies these savings. Excess solar generation can be stored rather than exported back to the grid at potentially lower rates or wasted. This stored solar energy can then be used later, reducing reliance on grid power during expensive peak times.
The 15% annual savings estimate is a conservative figure, often achievable through a combination of these strategies. For large commercial and industrial consumers, this translates into millions of dollars over the lifespan of the storage system, providing a rapid return on investment and a tangible boost to the bottom line. The financial advantages make advanced energy storage an attractive investment for forward-thinking businesses.
Policy and Market Drivers for Adoption by 2026
The accelerated adoption of advanced energy storage systems by 2026 is not solely driven by technological advancements and business benefits; it is also significantly propelled by supportive government policies, evolving market structures, and increasing corporate sustainability goals. These drivers create a fertile environment for widespread deployment.
Governments across the United States are recognizing the critical role of energy storage in achieving grid modernization, decarbonization targets, and enhanced energy security. This recognition is translating into a suite of incentives, mandates, and regulatory frameworks designed to encourage investment and deployment.
Key Policy and Market Influences
A combination of legislative action, financial incentives, and changing market dynamics is making energy storage an increasingly viable and attractive option for businesses and utilities alike.
- Federal Tax Credits and Grants: Investment Tax Credits (ITCs) for standalone storage and various grants are significantly reducing the upfront cost of deploying these systems.
- State-Level Mandates and Rebates: Many states have set ambitious energy storage targets and offer direct rebates or performance incentives for installation.
- Decarbonization Goals: Corporate and national commitments to reduce carbon emissions are driving investments in renewable energy paired with storage to ensure reliability.
- Wholesale Market Reforms: Reforms in wholesale electricity markets are increasingly valuing and compensating energy storage for its grid services, creating new revenue streams.
The growing emphasis on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria also plays a crucial role. Businesses are increasingly investing in sustainable energy solutions, including storage, not only for financial returns but also to enhance their public image, attract investors, and meet stakeholder expectations.
These policy and market drivers collectively create a powerful tailwind for energy storage adoption. By 2026, the regulatory landscape is expected to be even more favorable, making the economic case for advanced energy storage undeniable and accelerating its integration into the national energy infrastructure. This supportive ecosystem ensures that the benefits of grid resilience become accessible to a broader range of businesses.
Implementing Advanced Energy Storage: A Business Roadmap
For businesses considering advanced energy storage, a strategic roadmap is essential to ensure a successful implementation and maximize the projected 15% annual savings. The process involves careful planning, technology selection, financial analysis, and integration with existing energy infrastructure.
The first step is a comprehensive energy audit to understand current consumption patterns, peak demand, and potential vulnerabilities. This audit will inform the sizing and type of energy storage system best suited for the business’s specific needs and operational requirements.
Steps for Successful Deployment
A structured approach to implementing energy storage helps businesses navigate the complexities and achieve optimal outcomes. Each step is critical for realizing the full benefits of the investment.
- Energy Assessment: Analyze current energy usage, identify peak demand periods, and evaluate existing infrastructure.
- Technology Selection: Choose the appropriate storage technology (e.g., lithium-ion, flow battery) based on duration needs, power requirements, and budget.
- Financial Modeling: Conduct a detailed cost-benefit analysis, including potential savings from demand charges, time-of-use optimization, and incentives.
- Integration Planning: Plan for seamless integration with existing energy systems, including solar PV, generators, and building management systems.
- Permitting and Installation: Navigate local regulations and work with experienced installers to ensure safe and compliant deployment.
- Monitoring and Optimization: Implement advanced energy management software to continuously monitor performance, optimize operations, and track savings.
Engaging with experienced energy consultants and reputable technology providers is crucial throughout this process. Their expertise can help businesses navigate the technical complexities, identify eligible incentives, and design a system that delivers both resilience and financial returns. Furthermore, understanding the maintenance requirements and long-term performance guarantees of the chosen system is vital for sustained benefits.
By following this comprehensive roadmap, businesses can confidently embrace advanced energy storage, transforming their energy profile from a source of vulnerability to a strategic asset. The journey towards enhanced grid resilience and significant cost savings is a tangible goal for businesses in 2026.
| Key Aspect | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| Outage Prevention | Advanced energy storage ensures uninterrupted power supply, safeguarding critical business operations from grid failures. |
| Financial Savings | Businesses can achieve an estimated 15% annual savings through peak shaving, demand charge reduction, and energy optimization. |
| Enhanced Resilience | Storage systems fortify the grid against severe weather, cyber threats, and aging infrastructure, ensuring stability. |
| Policy Support | Government incentives and market reforms are driving rapid adoption and making storage more economically attractive. |
Frequently Asked Questions About Grid Resilience and Energy Storage
Grid resilience in 2026 refers to the ability of the electrical grid to withstand and rapidly recover from disruptions, such as extreme weather, cyberattacks, and equipment failures. It emphasizes proactive measures, including advanced energy storage, to minimize the impact of outages on businesses and communities.
Advanced energy storage systems prevent outages by providing instantaneous backup power when the main grid fails. They can also integrate into microgrids, allowing businesses to operate independently. This seamless transition ensures critical operations continue without interruption, protecting against financial losses and operational downtime.
Businesses can anticipate an estimated 15% annual savings by 2026. These savings are primarily achieved through strategies like peak shaving, where stored energy is used during high-cost periods, and demand charge reduction, lowering overall electricity bills significantly, particularly for large commercial users.
Yes, numerous government incentives exist, including federal Investment Tax Credits (ITCs) and various state-level rebates and grants. These policies aim to accelerate the adoption of energy storage by reducing upfront costs and making the technology more economically attractive for businesses and utilities.
Businesses with high energy consumption, critical operations, or those vulnerable to frequent outages benefit significantly. This includes manufacturing facilities, data centers, healthcare providers, and any enterprise where power continuity directly impacts productivity, revenue, and customer satisfaction, making resilience a top priority.
Conclusion
The path to enhanced grid resilience 2026 is unequivocally paved with advanced energy storage solutions. For businesses, this isn’t merely an environmental consideration but a strategic financial decision that promises substantial returns. By preventing costly outages and enabling an estimated 15% in annual savings through intelligent energy management, these systems are transforming operational vulnerabilities into powerful competitive advantages. As policies continue to evolve and technologies mature, integrating advanced energy storage will become an indispensable component of any forward-thinking business strategy, ensuring stability, sustainability, and economic prosperity in an increasingly dynamic energy landscape.





